The Early Social Indicator measures progress toward social competence in infants and toddlers, ages 6 months to 42 months of age. The ESI is a play-based observational measure of a child’s growth in social skills with toys, a familiar adult (and a peer if desired) during a 6-minute play period.
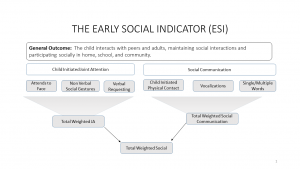
Six social key skills are observed during the assessment. Each of these key skills can be viewed individually as well as two composite scores that these key skills create: child initiated joint attention and social communication. These key skills were selected to comprise the ESI based on a conceptual review of the literature.
The key skill elements likely to evoke play and social interaction for Child Initiated Joint Attention are: Attends to Face, Non-Verbal Social Gestures, and Verbal Requesting. The key skill elements likely to evoke play and social interaction for Social Communication are: Child Initiated Physical Contact, Vocalizations, and Single/Multiple Words. This framework separates the refinements-expansions in socially expected behaviors in infants (i.e., smiles, gestures) from the positive verbal social behaviors expected of children 12 months and older (i.e., use of words in greetings, bids to play, requesting assistance, etc.). These positive nonverbal and verbal social behaviors are also expected to be distributed differently to adults, to peers, and to both persons (i.e., undirected). Young children interact more frequently with adults than peers, with with peer interaction and play emerging in older children.
